February 23, 2026
The Captions blog
Insights, guides and our latest product news.

All articles

Mirage achieves SOC 2 compliance

Add music to a video with Captions

How to write a winning AI video prompt

Video localization: Best practices for global brands

How to make an avatar from photos
Glossary: AI terms every content creator should know

Captions vs. subtitles: How to choose the best option
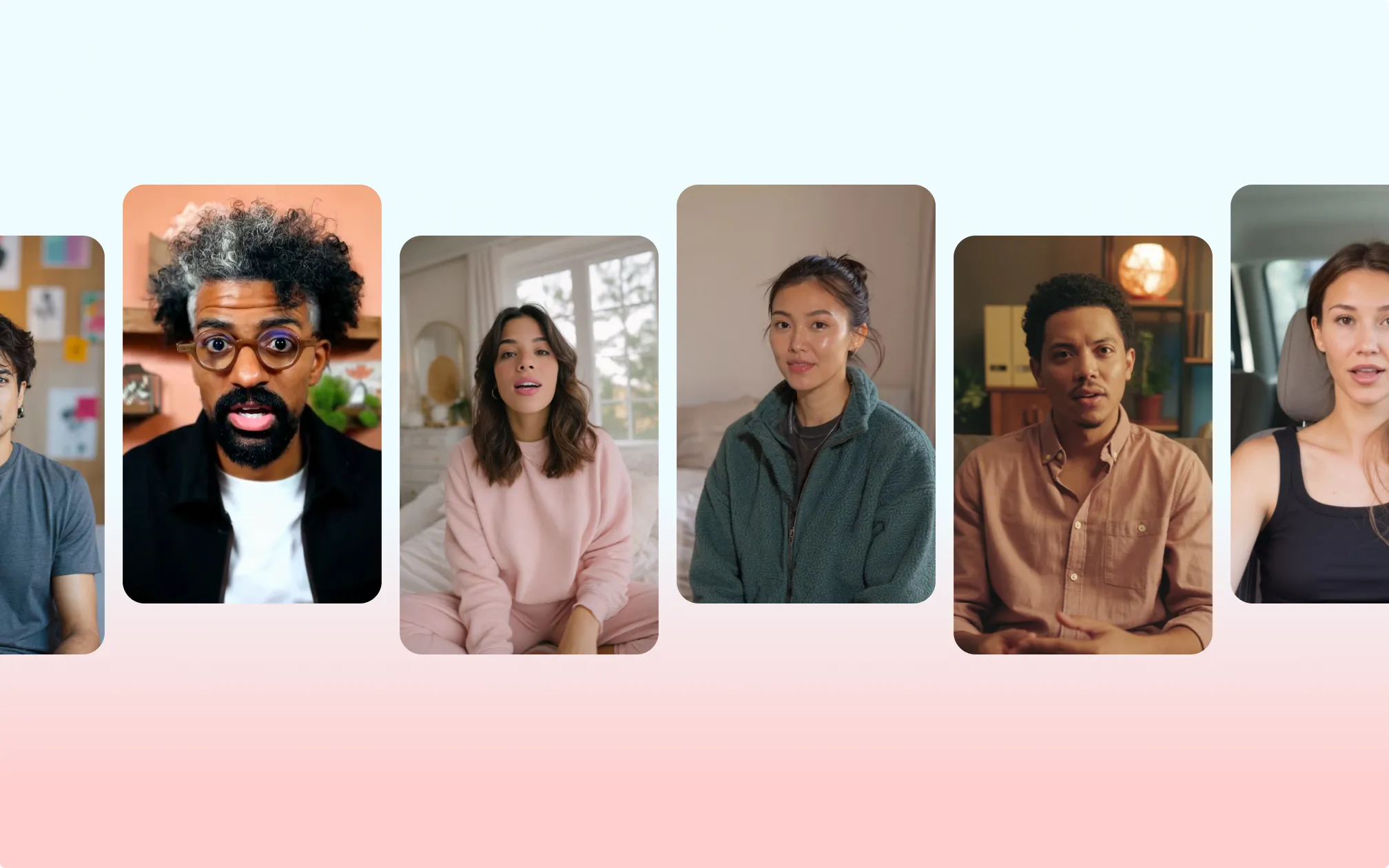

Why AI avatars are the future of scalable content
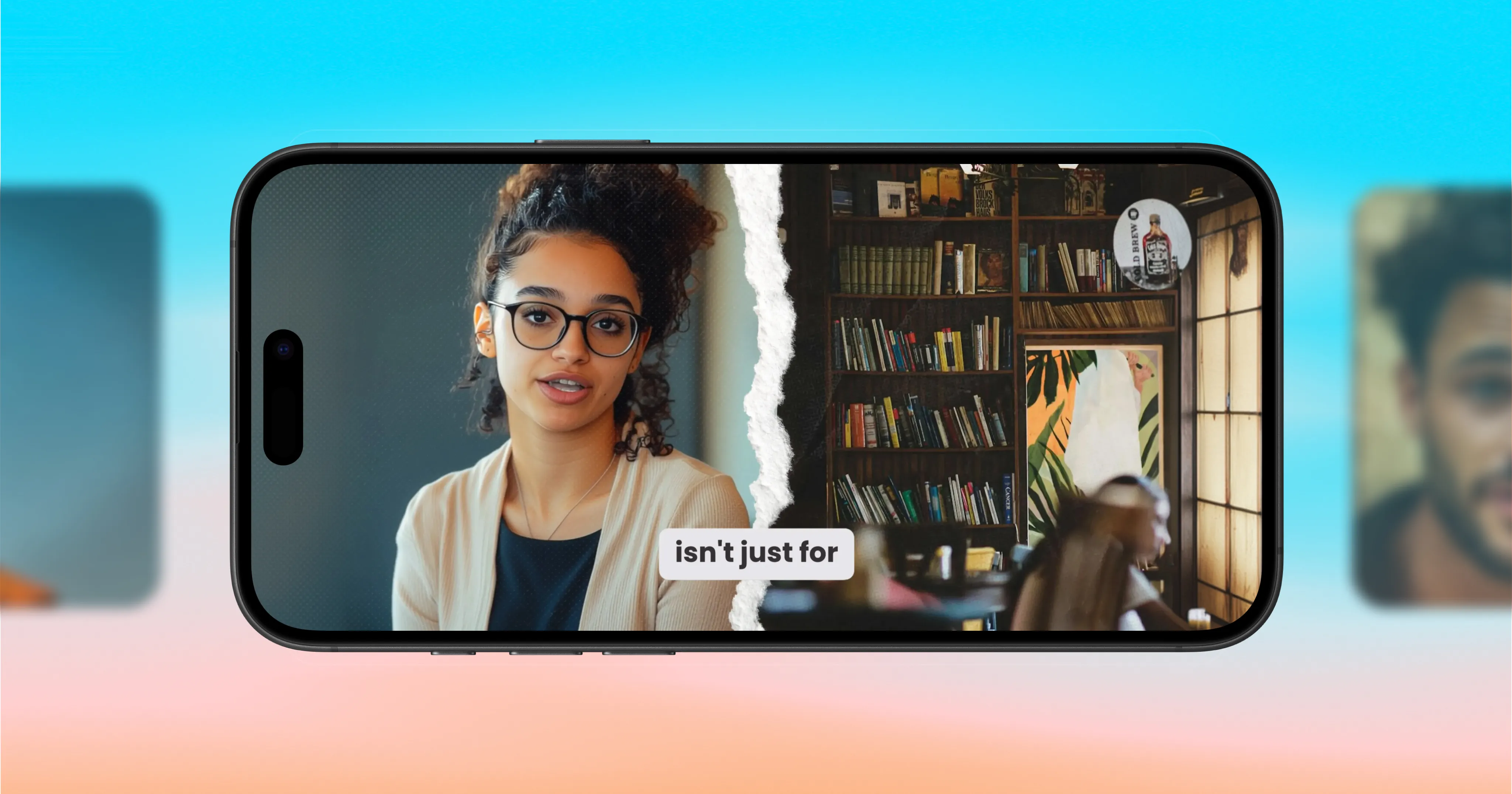

Captions brings one-tap video editing to horizontal formats
Easy tools for content clipping

Make your videos work harder: How to repurpose videos across needs and channels
9 TikTok ideas for businesses you can use today

How AI is changing video production

Find your video style with AI Edit

Shaping voices: Crafting expressive audio
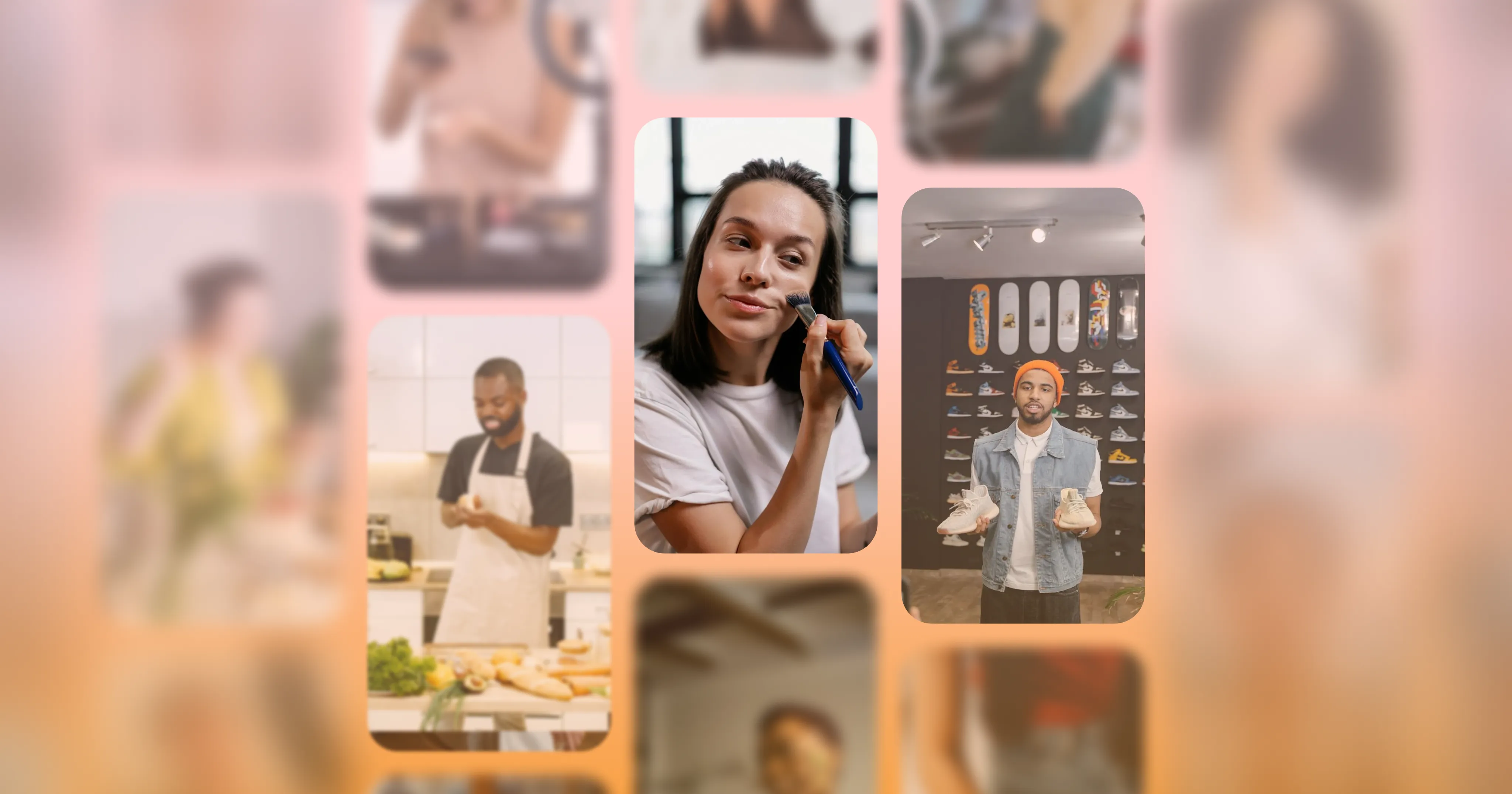

Tips for great UGC

A practical guide to B-roll

How to improve your video SEO strategy

How HubSpot built better campaigns with Mirage
Your guide to AI credits

Take a seat in the director's chair.

Editing videos is now as easy as typing.

Introducing Mirage: The future of video starts now.
How a startup improved their creative with Captions

We build synthetic humans. Here's what's keeping us up at night.
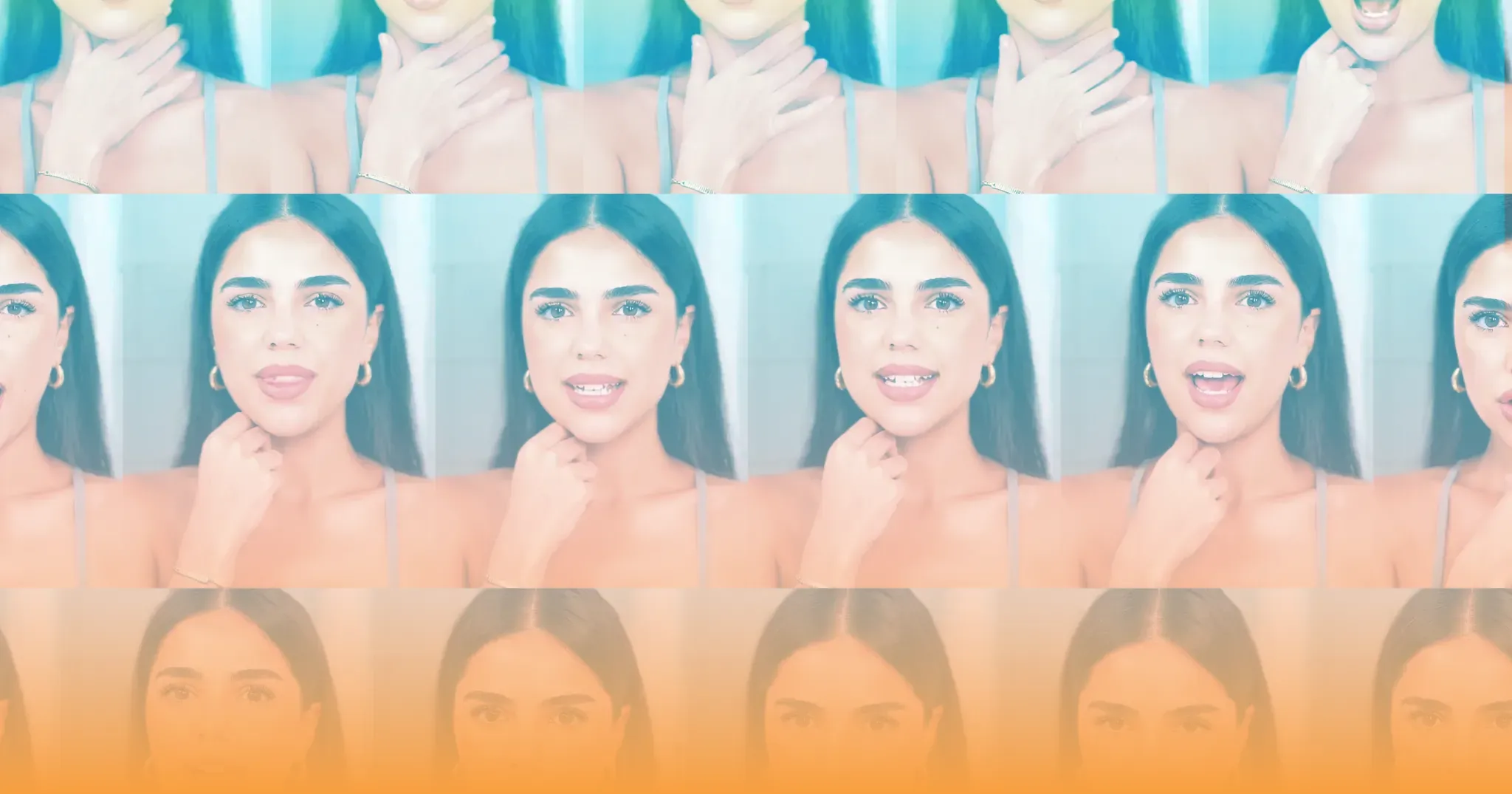

AI Video Is Inevitable. How It's Built Is Not.

Seeing voices: Foundation model research report

Mirage: The World's first foundation model for UGC video

Captions announces Series C to invest $100M in AI video research in New York.

Captions announces a $25 million Series B for our AI-powered creative studio

